Pose Estimation and Position-based Visual-servoing
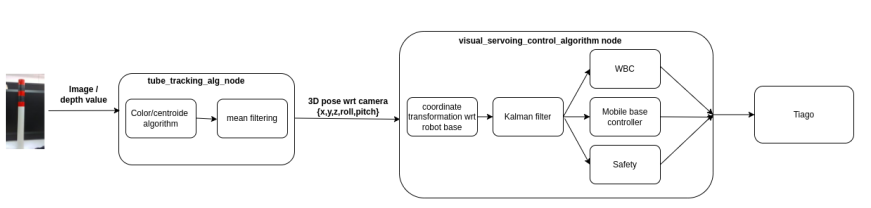
The project consist developing a strategy to control the position of the end-effector and the mobile base od the Tiago robot using visual servoing feedback from a stereo camera.
The idea of visual servoing consist of controlling the motion of a robot using information obtained from a computer vision feedback system. The visual data can come from a camera placed directly on the the robot’s end-effector(eye-in-hand configuration) or placed in a fixed position in the work space(fixed-camera configuration). The basic ideal of visual servoing consists of the minimization of an error value. The different visual-servoing techniques. differ with respect to the error function defined. In position-based image visual seroving(PBVS), the error function is specified based on position value in the robot task space. In Image-Based Visual servoing, the error function is defined in terms of image features. Although, IBVS is considered favorable compared to PBVS due to it low sensitivity to camera calibration errors, PBVS method was used. This is due to the limitation with respect to the control layer of the Tiago robot (Stevedan & Alberto, 2022).
The following shows one of the video experiments obtained during the project:
Some of the results of the experiments performed can be found below: